Bauerfeind MalleoLoc Ankle Brace MEDLEE
$ 239,99 $ 96,00
Stabilizing ankle orthosis for safe mobilization
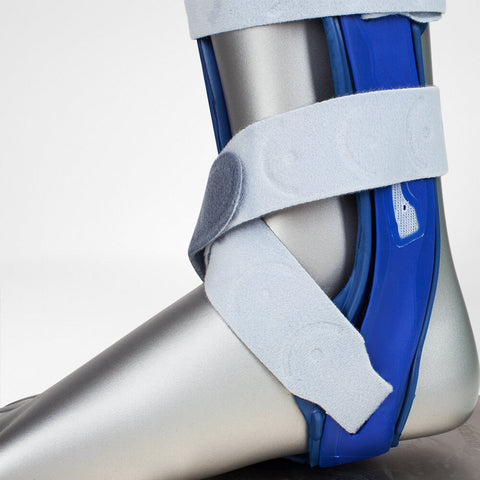
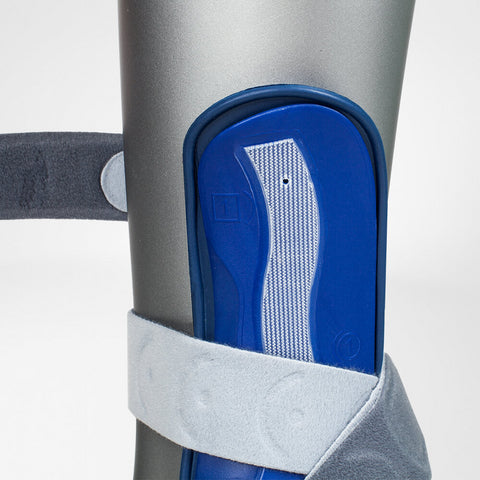
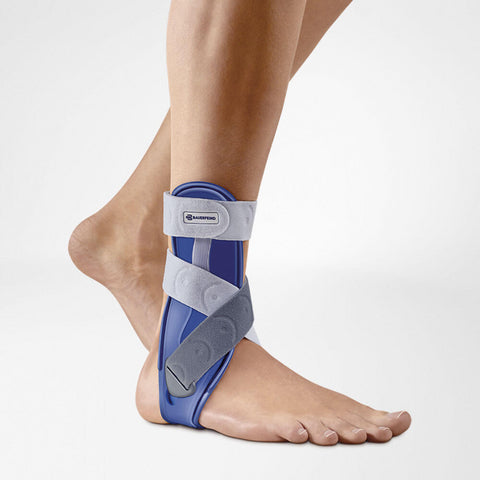
With an asymmetrical plastic splint, MalleoLoc reliably protects against further spraining, both inward and outward, even during exercise. It is positioned in front of the lateral malleolus and behind the medial malleolus, avoiding direct pressure on the malleoli. A protruding guide stimulates your foot muscles and counteracts incorrect movements, thereby actively stabilizing the ankle.
- Protects against sprains even during abrupt, powerful movement
- Stabilizes the ankle with or without shoes
- Supports natural heel-to-toe movement of the foot for mobilization
Protection and stability with or without shoes
After an injury, following surgery or in case of chronically weakened ligaments, your ankle needs particular protection. With an asymmetrical plastic splint, MalleoLoc reliably protects against further spraining, both inward and outward, even during exercise. It is positioned in front of the lateral malleolus and behind the medial malleolus. In this way, it prevents direct pressure on the malleoli.
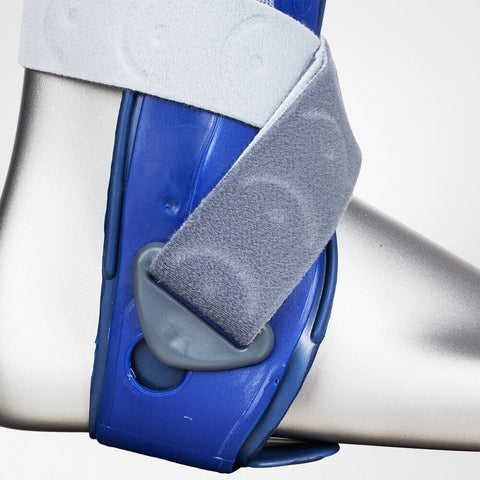
The splint is softly cushioned on the inside. A protruding guide in the sole area stimulates your foot muscles, thereby actively stabilizing the ankle. If required, the orthotist at your medical supply retailer can adapt the orthosis to your anatomy.
Fit again fast
MalleoLoc is secured with two crossed Velcro straps. By pulling the straps as tight as is comfortable, you can control your own stability. The gentle pressure and high degree of security make the support comfortable to wear.
At the same time, MalleoLoc helps your body to help itself: despite your weakened ligaments, it’s important that you stay active and strengthen your muscles. Thanks to its slim fit, you can wear MalleoLoc in almost all firm footwear, allowing you to move correctly and without fear during everyday activities. All this boosts recovery: after all, being active is key to good health!
Measurement and product range


Indications
- Early functional treatment for injuries of the lateral malleolar ligaments (and the bifurcate ligaments)
- Capsular ligament strains
- Postoperative rehabilitation
- Chronic ligament insufficiency
*The brace may be covered under your extended health insurance.
| Size | 1, 2 |
|---|
Prompt Shipping and professional packaging
We offer a broad range of shipping options thanks to our long-standing relationships with UPS, FedEx and DHL. Our warehouse personnel will pack every item to our exacting specifications. Your goods will go through an extensive inspection and will be adequately secured before being shipped. We ship to thousands of customers each day across different countries. The fact that we are committed to becoming the biggest online retailer in the World is obvious. Both Europe as well as the USA have distribution and warehouse centers.
Orders that contain more than one item are assigned processing times in accordance with the item.
Prior to shipment, all purchased products will be thoroughly inspected. Most orders are now shipped within 48 hours. The delivery estimate is 3 to 7 days.
Returns
We don't manage the stock at our factory and warehouse. So the actual stock may fluctuate at any moment. It's possible that the stocks could be depleted after your order has been placed.
Our policy lasts for 30 days. We cannot return or exchange your purchase if it has been 30 days from the date of purchase.
To be considered eligible for return it must be in its original packaging, unopened and in the condition you received it. The item must be in the original packaging.
Related products
Health Care
RESUSCITATOR SMART BAG ADULT INFLATED CUFFED MASK WITH RESERVOIR AND 7FT OXYGEN TUBING MEDLEE
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care
Health Care